Introduction
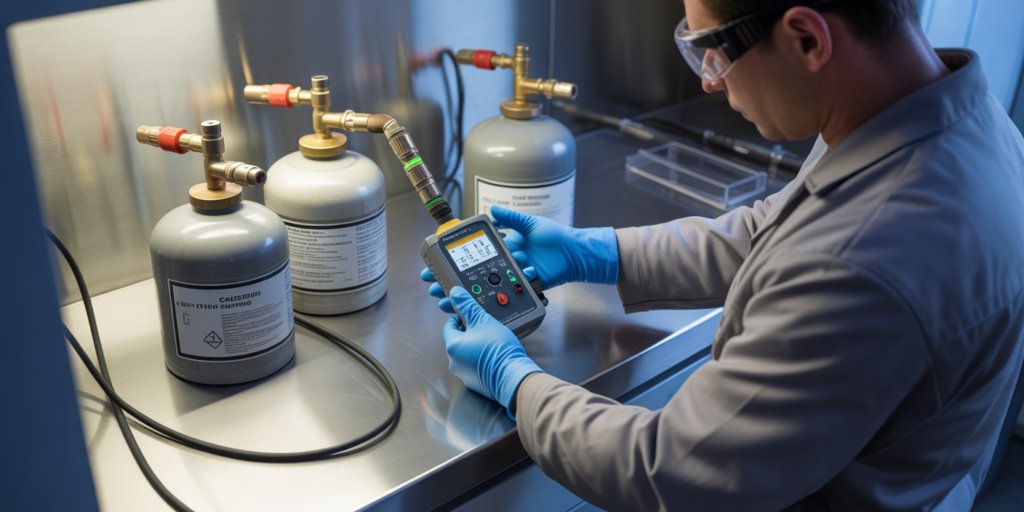
Gas detectors are a frontline defense for workplace safety in industries like oil and gas, chemical manufacturing, mining, and confined space operations. They detect hazardous gases—such as carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, methane, or volatile organic compounds—alerting personnel to potentially life-threatening situations. However, these vital devices can only protect workers if they are properly calibrated.
Why Gas Detector Calibration Is Critical
- Worker Safety: Incorrect readings can expose workers to toxic or explosive gases, with potentially fatal consequences.
- Regulatory Compliance: OSHA, MSHA, and other agencies require regular calibration and maintenance of gas detection equipment.
- Incident Prevention: Accurate detectors help prevent costly shutdowns, environmental releases, and damage to reputation.
A miscalibrated detector could fail to alert workers to a dangerous gas leak, leading to severe injury, loss of life, or regulatory penalties.
Factors Affecting Gas Detector Accuracy
- Sensor Degradation: Sensors naturally degrade over time, especially when exposed to harsh environments or high gas concentrations.
- Environmental Conditions: Temperature, humidity, and pressure fluctuations can affect detector response.
- Bump Testing and Calibration Drift: Regular exposure to test gases (bump tests) and calibration drift both impact accuracy.
- Contamination: Dust, water, or chemicals can clog or damage sensors.
Calibration Best Practices
1. Follow Manufacturer Recommendations
Most manufacturers recommend calibration every 30 to 90 days, with more frequent checks in harsh or critical environments.
2. Bump Testing
Conduct a functional (bump) test before each use to ensure the detector responds to gas exposure.
3. Full Calibration
Perform a full calibration regularly using certified calibration gases. This adjusts the detector’s internal settings for accuracy.
4. Documentation and Traceability
Maintain logs of calibration and bump tests, including dates, results, and any corrective actions. Digital records simplify audits and compliance checks.
5. Use Certified Calibration Gases
Always use gases with known, traceable concentrations for calibration—expired or incorrect gases can compromise results.
Real-World Examples
On a refinery site, a gas detector that hadn’t been calibrated in six months failed to sound an alarm during a hydrogen sulfide leak. The oversight was caught in time, but it prompted a site-wide review and overhaul of the entire calibration program.
In mining, improperly calibrated methane detectors have led to undetected leaks and catastrophic explosions, underscoring the life-or-death importance of routine calibration.
Actionable Tips
- Assign responsibility for calibration and bump tests to specific personnel
- Maintain a calibration schedule and automate reminders
- Store detectors and calibration gases according to manufacturer specs
- Quarantine detectors immediately if calibration fails or is overdue
- Train workers to recognize detector malfunctions and respond appropriately
Why SIMCO?
SIMCO provides:
- On-site calibration for minimal downtime
- Calibration for single and multi-gas detectors
- Compliant documentation for audits
- Expert advice on calibration intervals and best practices
Conclusion
Calibrating gas detectors is a non-negotiable part of workplace safety and regulatory compliance. By establishing robust calibration protocols and working with trusted providers like SIMCO, you help ensure every worker goes home safely at the end of the day.