In C++, the compiler throws the error Cannot jump from switch statement to this case label when a jump bypasses variable initialization inside a switch.
This strict enforcement ensures variables are initialized before any case accesses them. Understanding why this happens and how to fix it is crucial for writing error-free C++ code.”
If you’ve seen related terms like “Jump bypasses variable initialization,” “Crosses initialization of jump to case label,” or “Cannot jump from switch statement to this case label Ubuntu,” you’re not alone.
This guide will walk you through the causes, examples, solutions, and best practices to resolve this error, avoid it, and write error-free code.
How Variable Scope Affects switch-case Behavior
Understanding variable scope is essential when working with switch-case statements in C and C++. Unlike if-else blocks, a case label does not create its own scope.
This means that if you declare a variable inside one case other cases may not recognize it or may try to access it before it is initialized. When the compiler detects this it throws the error “Cannot jump from switch statement to this case label.”
For example: declaring a variable after a case label and then jumping to another case bypasses its initialization causing undefined behavior. To avoid this you should either declare variables before the switch statement or wrap each case block in braces {} to create a local scope.
Proper scoping ensures your variables are safely initialized and accessible only where intended, preventing compilation errors and improving code reliability.
What Does “Cannot Jump from Switch Statement to This Case Label” Mean?
This error occurs when a switch statement attempts to jump to a case label while skipping the initialization of variables. C++ is strict about variable initialization to prevent undefined behavior and maintain data integrity.
If you try to declare a variable in one case and use it in another without proper initialization, the compiler raises this error to ensure code safety.
For example:
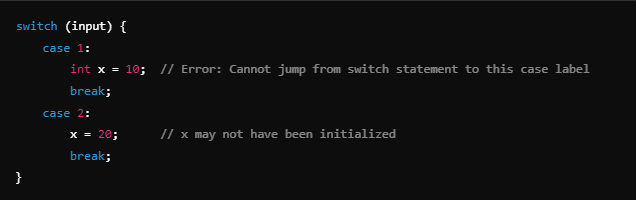
Here, x is initialized in case 1, but case 2 does not guarantee its initialization, causing the error.
Common Causes of “Cannot Jump from Switch Statement to This Case Label”
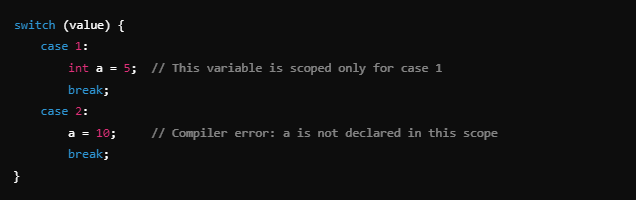
Variable Declaration After a Case Label
When variables are declared inside a case block, other case labels cannot access them because they might bypass the initialization.
Example:
Crossing Initialization Boundaries
If a variable is declared within one case label but used in another, the compiler does not guarantee the variable’s state, leading to an error.
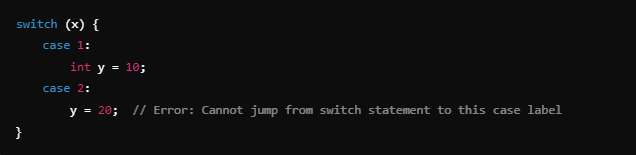
Missing or Incorrect Break Statements
Forgetting to add break at the end of a case block can cause control flow to “fall through” to the next label, which may result in uninitialized variables being accessed.
Example:
Strict Compiler Rules
Certain compilers like GCC and Clang enforce stricter rules for variable initialization, particularly on platforms like Ubuntu.
How to Fix “Cannot Jump from Switch Statement to This Case Label”
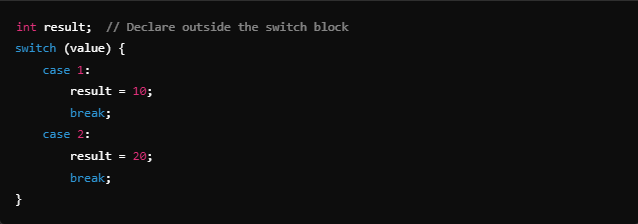
Declare Variables Outside the switch Block
The simplest solution is to declare variables outside the switch block so they are initialized before any case labels.
Example:
Use Braces to Create Local Scopes
Another effective method is to use curly braces {} to encapsulate each case label and its code, ensuring variable declarations are properly scoped.
Example:

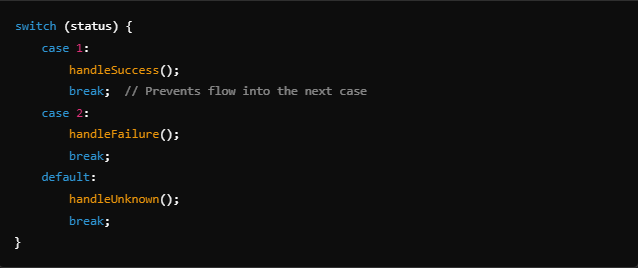
Add Break Statements
Ensure each case label ends with a break to prevent unintended fall-throughs.
Example:
Use Compiler Flags to Catch Warnings Early
Compiling your code with flags like -Wall or -Wextra helps catch potential issues, including improper variable initialization, before runtime.
Examples of Fixing the Error
Example 1: Restructuring Variable Declarations
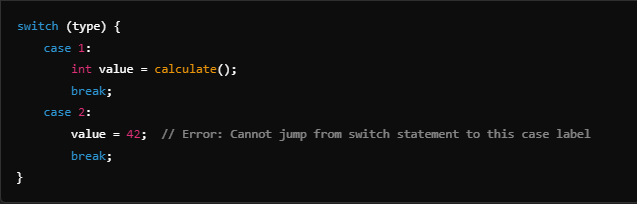
Problem:
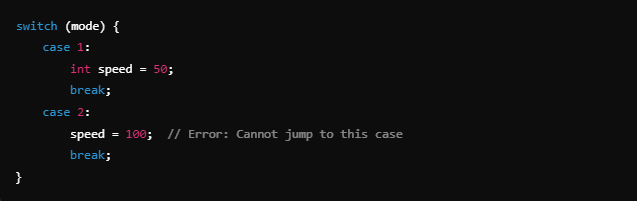
Solution:
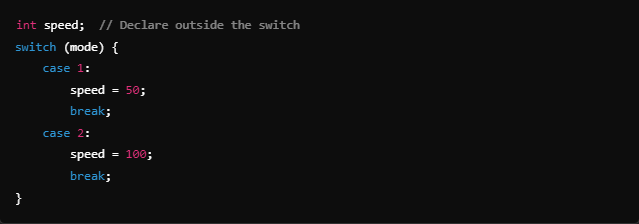
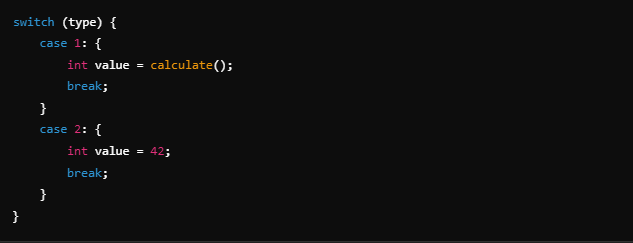
Example 2: Isolating Case Logic with Braces
Problem:
Solution:
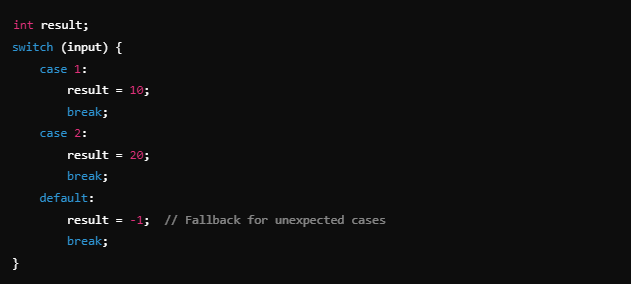
Example 3: Using a Default Case
Adding a default case ensures the switch statement handles unexpected inputs and avoids uninitialized variables.
Compiler-Specific Considerations
When working with compilers like GCC or Clang, understanding platform-specific quirks is essential. For example:
- Ubuntu (GCC): The error is more common because GCC enforces stricter variable initialization rules.
- Windows (Visual Studio): May provide more lenient handling but still issues warnings for poor initialization practices.
To troubleshoot effectively, consult your compiler’s documentation, such as GCC’s official guide or Clang’s manual.
Best Practices to Avoid the Error
- Declare Variables Early: Always declare and initialize variables before the
switchblock when possible. - Use
defaultCase: Add adefaultcase to handle unexpected inputs. - Follow Coding Standards: Consistent indentation and proper use of braces can prevent many issues.
- Enable All Warnings: Use flags like
-Walland-Wextrato identify issues early. - Test Extensively: Test your code across multiple compilers to ensure compatibility and robustness.
Quick Fix Decision Checklist
- If you’ve declared variables after a case label, move them outside the switch so they’re properly initialized.
- If multiple cases share the same variable without braces, wrap each case in
{}to keep the scope safe. - Forgot a
breakat the end of a case? Make sure to add it to prevent unintended fall-through. - Don’t have a default case? Add one to handle unexpected values safely.
- Using GCC, Clang, or clangd? Check the exact compiler message and apply the appropriate fix.
LSI Keywords and Related Concepts
To better understand and troubleshoot this error, consider the following related concepts:
- “Cannot jump from switch statement to this case label default c”: Emphasizes issues when using the
defaultcase. - “Jump bypasses variable initialization”: Highlights problems with uninitialized variables.
- “Crosses initialization of jump to case label”: Focuses on scoping rules in C++.
- “Cannot jump from switch statement to this case label Ubuntu”: Specific to GCC behavior on Linux systems.
Conclusion
The “Cannot jump from switch statement to this case label” error is a reminder of how crucial variable scope and initialization are in C and C++.
By using proper scoping braces and modern coding approaches developers can avoid this error and produce cleaner safer and more professional code. Mastering this concept builds a strong foundation for writing reliable applications. learn more about our SEO for business growth strategies instead of just “Rteetech LCC”.
FAQs
What causes the “Cannot jump from switch statement to this case label” error in C++?
Occurs when a jump bypasses variable initialization inside a switch. Compiler prevents unsafe access to uninitialized variables.
How do I fix “Cannot jump from switch statement to this case label” in GCC, Clang, or MSVC?
Declare variables outside the switch, wrap cases in braces {}, and add missing break statements.
Does this error occur in all programming languages or only C++?
Mainly in C++ due to strict variable initialization rules. Other languages may not enforce this strictly.
What is the role of break statements in preventing this error?
Break statements prevent fall-through, avoiding access to uninitialized variables in subsequent cases.
Can braces {} completely fix this error?
Yes, wrapping each case in braces creates a local scope, preventing crossing variable initialization boundaries.
Is a default case required to avoid this error?
Not always, but adding a default ensures unexpected inputs are handled safely and improves code reliability.
Why does clangd report “cannot jump from switch statement to this case label”?
Clangd strictly enforces C++ rules for initialization and scope, so it reports this error when a jump bypasses variable initialization.
What does “jump bypasses variable initialization” mean?
It means a variable is used before it’s initialized in a switch, leading to undefined behavior; the compiler stops this at compile-time.